Drone sightings around the world are rapidly increasing, prompting significant global interest. This phenomenon necessitates a comprehensive analysis considering geographic distribution, drone types, operational motivations, societal impact, technological advancements, and associated security and privacy concerns. Understanding these multifaceted aspects is crucial for developing effective regulatory frameworks and mitigating potential risks.
This study examines the global landscape of drone sightings, analyzing data from various regions to identify trends and patterns. We investigate the types of drones involved, their capabilities, and the motivations behind their deployment, ranging from commercial applications to malicious activities. Furthermore, we assess the societal impact of increased drone activity, considering public perception, governmental responses, and legal ramifications.
Finally, we explore technological advancements in drone technology and their implications for future sightings.
Geographic Distribution of Drone Sightings
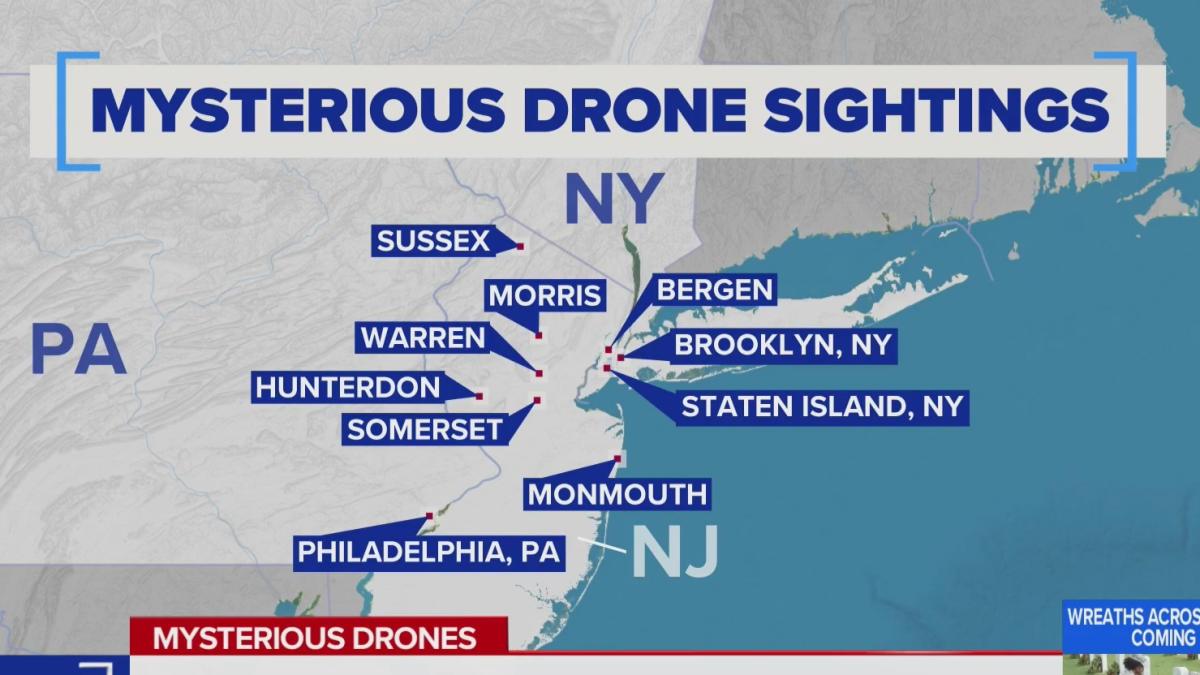
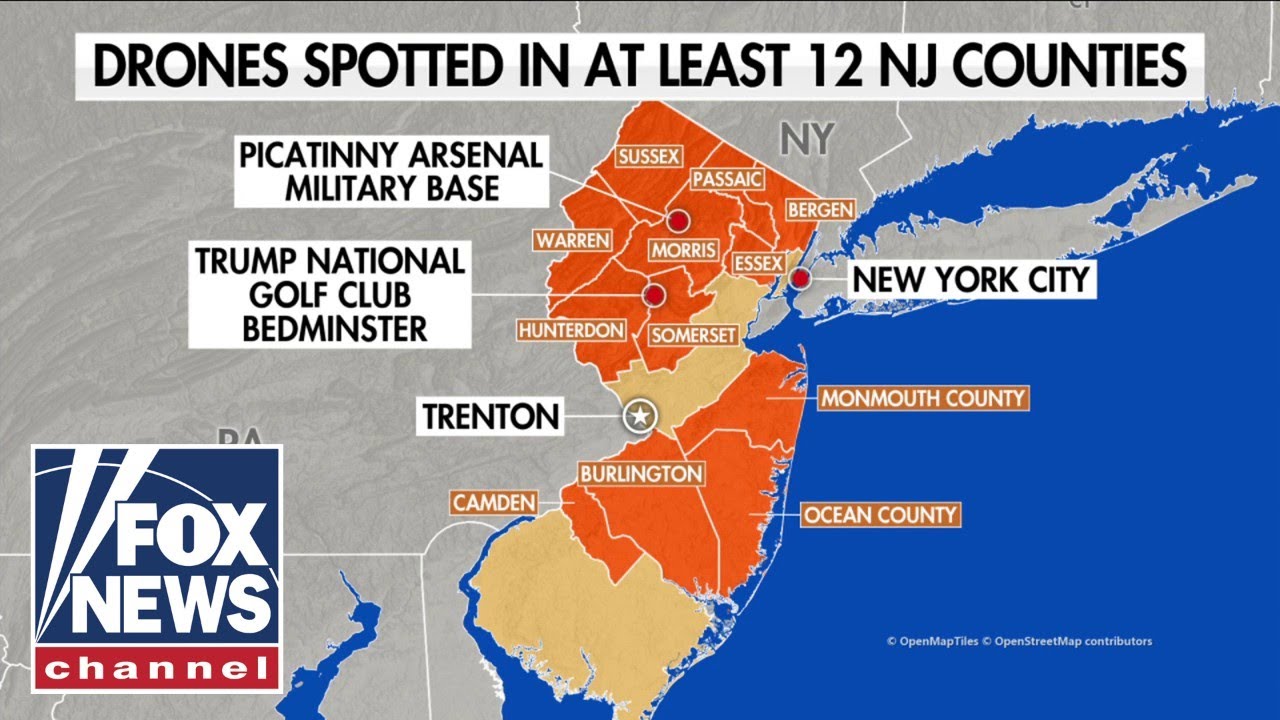
The global distribution of drone sightings exhibits significant geographical variation, influenced by factors such as population density, regulatory frameworks, technological accessibility, and the prevalence of specific drone applications. Analysis of reported sightings reveals distinct patterns and hotspots, offering insights into the spatial dynamics of drone technology deployment and its associated challenges.
A comprehensive analysis of reported drone sightings requires a global perspective, considering variations in reporting mechanisms and data availability across different regions. While a precise world map illustrating sighting frequency with color-coding is beyond the scope of this text-based response, a conceptual representation can be envisioned. A hypothetical map would show darker shades of red in areas with high sighting density, transitioning to lighter shades and ultimately to white in areas with few or no reported sightings.
The legend would correlate color intensity with a numerical range representing the number of sightings per unit area (e.g., per square kilometer).
Regions with High Concentrations of Drone Sightings and Explanations
Areas with high population density, such as major metropolitan centers in North America, Europe, and East Asia, generally exhibit higher concentrations of reported drone sightings. This is primarily attributed to the increased likelihood of drone operation within these densely populated areas, driven by factors like commercial applications (delivery services, aerial photography), recreational activities, and potentially illicit uses. Furthermore, robust reporting mechanisms and media attention in these regions may contribute to a higher number of reported incidents.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate enhanced surveillance measures at critical infrastructure. Real-time monitoring systems, such as the ambassador bridge camera , provide valuable data for analyzing drone activity patterns near sensitive locations. This data contributes to a broader understanding of drone usage and potential threats, informing strategies to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized drone operations worldwide.
Conversely, regions with less developed infrastructure, lower population density, or stricter regulations may show lower sighting frequencies, although this doesn’t necessarily reflect actual drone usage.
Comparison of Drone Types Across Geographic Locations
The types of drones sighted vary considerably depending on the geographic location and its associated applications. In developed nations, a higher proportion of sightings might involve commercially manufactured drones with advanced features, reflecting the widespread availability and use of such technology. These might include drones designed for aerial photography, mapping, delivery services, or surveillance. In contrast, regions with less developed infrastructure may exhibit a higher proportion of smaller, less sophisticated drones, possibly reflecting a lower cost of entry into the drone market and limited access to advanced technologies.
Furthermore, the prevalence of specific drone models may be influenced by local regulations and import/export restrictions.
Geographic Distribution of Drone Sightings: Data Table
The following table presents a hypothetical representation of drone sighting data, highlighting regional differences. Note that actual data collection and reporting methodologies vary widely, impacting the accuracy and comparability of such statistics across regions.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate enhanced surveillance measures at critical infrastructure. The security concerns surrounding such unauthorized aerial activity are heightened in locations like the Ambassador Bridge, prompting the implementation of advanced monitoring systems, such as the ambassador bridge camera system. This technology contributes to a broader strategy for mitigating the risks associated with worldwide drone incursions into restricted airspace.
| Region | Number of Sightings | Predominant Drone Type | Potential Explanations |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America (Urban Centers) | High | Commercial, multirotor, advanced features | High population density, commercial applications, robust reporting |
| Europe (Rural Areas) | Moderate | Small, fixed-wing, recreational | Widespread recreational use, less stringent regulations in certain areas |
| East Asia (Major Cities) | High | Commercial, diverse models, some illicit use | High population density, diverse applications, potential for unregulated operations |
| Sub-Saharan Africa (Rural Areas) | Low | Basic, low-cost models | Limited access to advanced technology, fewer commercial applications |
Types of Drones Involved in Sightings: Drone Sightings Around The World
Drone sightings worldwide involve a diverse range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), reflecting the expanding commercial, recreational, and military applications of this technology. Understanding the types of drones involved is crucial for analyzing sighting patterns, assessing potential risks, and implementing effective regulatory measures. This section details the most commonly sighted drone models and manufacturers, their capabilities, and technical specifications.The prevalence of specific drone models varies geographically depending on factors such as local regulations, accessibility, and market trends.
However, certain manufacturers and models consistently appear in reports of drone sightings globally.
Commonly Sighted Drone Models and Manufacturers
Several manufacturers dominate the market for drones frequently involved in sightings. DJI, Autel Robotics, and Parrot are among the leading producers of consumer and commercial drones, with their models frequently appearing in reports of both authorized and unauthorized flights. Military-grade drones, while less frequently reported in public sightings, are often manufactured by companies specializing in defense technology, including but not limited to Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and General Atomics.
Drone Capabilities and Potential Uses
The capabilities of drones vary widely depending on their design and intended use. Commercial drones often feature high-resolution cameras for aerial photography and videography, advanced sensors for mapping and surveying, and payload capacity for delivery or inspection tasks. Recreational drones typically prioritize ease of use, flight time, and camera quality, while military drones are designed for surveillance, reconnaissance, and even offensive capabilities, including the deployment of weapons.
The potential uses of these diverse drone types contribute to the range of scenarios in which they are sighted.
Description of Drone Types
The following provides a description of three frequently sighted drone types, focusing on size, features, and range:
- DJI Mavic 3: This compact, foldable drone offers high-resolution imaging capabilities (up to 5.7K video) and advanced obstacle avoidance systems. Its range typically extends to several kilometers depending on environmental conditions. It is frequently used for aerial photography, videography, and inspection work. Its size is relatively small, making it easily portable.
- Autel Robotics EVO II Pro: Known for its robust design and long flight time, the EVO II Pro is often employed in commercial applications such as agriculture, construction, and public safety. It features a high-resolution camera with various lens options and supports multiple payload configurations. Its size is larger than the Mavic 3, offering increased stability and payload capacity. Range varies based on signal strength and environmental factors.
- Parrot Anafi USA: This drone is a lighter, more compact option often chosen for recreational use. It offers good image quality and ease of use. Its range is generally shorter than the other two mentioned. Its smaller size contributes to its portability and ease of use for casual users.
Technical Specifications Comparison
The following table compares the technical specifications of the three drone types discussed above. Note that specifications may vary slightly depending on the specific model and configuration.
| Specification | DJI Mavic 3 | Autel Robotics EVO II Pro | Parrot Anafi USA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Flight Time | 46 minutes | 40 minutes | 25 minutes |
| Maximum Range | 15 km (FCC), 8 km (CE) | 9 km | 4 km |
| Weight | 895 g | 1100 g | 320 g |
| Camera Resolution (Video) | 5.7K | 8K | 4K |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Yes (multi-directional) | Yes (multi-directional) | Yes (limited) |
Array
The proliferation of drones globally presents significant security and privacy challenges. Unauthorized drone operations pose risks to critical infrastructure, public safety, and individual privacy, necessitating the development and implementation of effective detection and mitigation strategies. The potential for malicious use, coupled with the inherent difficulties in tracking and identifying drones, underscores the urgency of addressing these concerns.Unauthorized drone operations present a range of security risks.
These risks extend beyond simple nuisance and trespass, encompassing threats to national security, critical infrastructure, and public safety.
Security Risks Associated with Unauthorized Drone Operations
Unauthorized drone flights near airports, for instance, can disrupt air traffic, potentially leading to collisions and significant loss of life. Similarly, drones carrying explosives or other harmful materials could be used to target critical infrastructure, such as power plants or government buildings, causing widespread damage and disruption. Furthermore, the potential for drones to be used for surveillance or reconnaissance by malicious actors, including state-sponsored groups or criminal organizations, poses a significant threat to national security.
The covert nature of drone operations makes detection and response challenging, increasing the potential for successful attacks. The lack of clear regulations and enforcement mechanisms in many regions further exacerbates these security vulnerabilities. Consider, for example, the potential for a drone to deliver a small explosive device to a crowded public space, causing significant casualties and widespread panic.
This scenario highlights the need for robust security measures to prevent and mitigate such threats.
Privacy Violations Resulting from Drone Surveillance
The widespread use of drones for surveillance raises significant privacy concerns. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and other sensors can capture highly detailed images and videos of individuals and their properties without their knowledge or consent. This capability allows for pervasive surveillance that could be used to track individuals’ movements, monitor their activities, and even identify their identities. The lack of clear legal frameworks governing the use of drones for surveillance in many jurisdictions further exacerbates these concerns, leaving individuals vulnerable to unauthorized monitoring and potential misuse of their personal information.
The potential for this technology to be used for stalking, harassment, or even targeted intimidation is significant. For instance, a drone equipped with facial recognition technology could be used to identify and track individuals without their knowledge or consent, raising serious ethical and legal implications.
Methods for Detecting and Mitigating Unauthorized Drone Activity, Drone sightings around the world
Several methods are employed to detect and mitigate unauthorized drone activity. These range from electronic countermeasures (ECM) such as jamming and spoofing, to physical measures such as nets and radar systems. Advanced detection systems use radio frequency (RF) sensors to identify and track drones based on their communication signals. Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are being developed to enhance the accuracy and speed of drone detection and identification.
These systems can analyze various data sources, including radar, camera, and acoustic data, to identify and classify drones and their intended actions. Moreover, geofencing technologies can be used to restrict drone access to sensitive areas, while counter-drone systems are being deployed to neutralize or capture unauthorized drones. However, the effectiveness of these systems is contingent upon their technological capabilities, as well as the sophistication of the methods used to circumvent them.
The ongoing technological arms race between drone operators and counter-drone technologies necessitates continuous adaptation and innovation.
Malicious Use of Drones and Countermeasures
Drones can be weaponized in various ways, posing significant threats. They can be used to deliver explosives, toxic substances, or other harmful materials to targeted locations. Furthermore, drones can be equipped with advanced sensors and cameras for surveillance and reconnaissance purposes, facilitating espionage and other malicious activities. Countermeasures include the deployment of anti-drone technologies, such as radar systems, jammers, and net-launching systems.
These systems aim to detect, track, and neutralize hostile drones before they can reach their targets. Furthermore, strengthening cybersecurity measures to prevent unauthorized access and control of drones is crucial. Robust encryption and authentication protocols can help protect drones from hacking and malicious control. The development of AI-powered systems for autonomous drone detection and neutralization is also underway.
These systems promise to improve the speed and efficiency of counter-drone operations, enhancing overall security.
The proliferation of drone sightings worldwide presents a complex challenge requiring a multi-faceted approach. While drones offer significant benefits across various sectors, their unregulated use poses substantial risks to security and privacy. Further research into the technological advancements driving this increase, coupled with the development of robust regulatory frameworks, is essential to harness the positive potential of drones while mitigating their inherent dangers.
International cooperation and data sharing are crucial for a comprehensive understanding and effective management of this evolving landscape.
Query Resolution
What are the most common causes of unauthorized drone flights?
Unauthorized drone flights stem from various sources, including recreational misuse, deliberate malicious intent, and accidental operational errors. Lack of awareness regarding airspace restrictions and regulations also contributes significantly.
How are governments addressing the rise in drone sightings?
Governmental responses vary, encompassing the implementation of stricter regulations, investment in counter-drone technologies, public awareness campaigns, and increased collaboration between agencies to enhance surveillance and enforcement.
What are the long-term implications of widespread drone use?
Widespread drone use presents both opportunities and challenges. Potential benefits include enhanced efficiency in various sectors, improved infrastructure monitoring, and advancements in emergency response. However, concerns regarding privacy violations, security threats, and environmental impact require careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies.
